Oral Paper Presentation
Annual Scientific Meeting
Session: Plenary Session 4B - IBD / Obesity / Stomach / Pediatrics
73 - Dupilumab Improves Histologic and Endoscopic Aspects of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE), as Well as Rate of Weight Gain, in Children Aged 1 to <12 years: 52-week Results From the Phase 3 EoE KIDS Trial (Late-Breaking Abstract)
Wednesday, October 25, 2023
9:50 AM - 10:00 AM PT
Location: Ballroom B
- MC
Mirna Chehade, MD, MPH
New York, NY
Late Breaking Abstract Presenter(s)
Mirna Chehade, MD, MPH1, Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH2, Jonathan M. Spergel, MD, PhD3, Marc E. Rothenberg, MD, PhD4, Robert D. Pesek, MD5, Margaret H. Collins, MD4, Ikuo Hirano, MD6, Ruiqi Liu, PhD7, Elizabeth Laws, PhD8, Eric Mortensen, MD7, Renata Martincova, MD9, Jennifer Maloney, MD7, Eilish McCann, PhD7, Matthew P. Kosloski, PharmD, PhD7, Jennifer D. Hamilton, PhD7, Carin Samuely, MD7, Lila Glotfelty, MD, PhD8, Arsalan Shabbir, MD, PhD7; 1Mount Sinai Center for Eosinophilic Disorders, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 2University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 3Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA; 4Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, OH; 5University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences and Arkansas Children's Hospital, Little Rock, AR; 6Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL; 7Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Tarrytown, NY; 8Sanofi, Bridgewater, NJ; 9Sanofi, Prague, Czech Republic
Introduction: There are no approved treatments for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) in children aged <12 years. Dupilumab blocks key type 2 inflammation drivers and is approved for EoE in patients (pts) aged ≥12 years and weighing ≥40kg in the USA. The Phase 3 EoE KIDS trial (NCT04394351) evaluated efficacy and safety of dupilumab in pts aged 1 to <12 years with EoE.
Methods: Part A was a 16 week (W), placebo-controlled study; pts were randomized 2:2:1:1 to weight-tiered, subcutaneous dupilumab on a higher-exposure (HE) or lower-exposure (LE) regimen, or placebo (2 groups). Patients who completed Part A could enter Part B, in which pts continued the same dupilumab regimen and pts on placebo switched to their pre-assigned HE or LE dupilumab dose to W52. This analysis includes pts assigned to HE dupilumab and placebo up to W52.
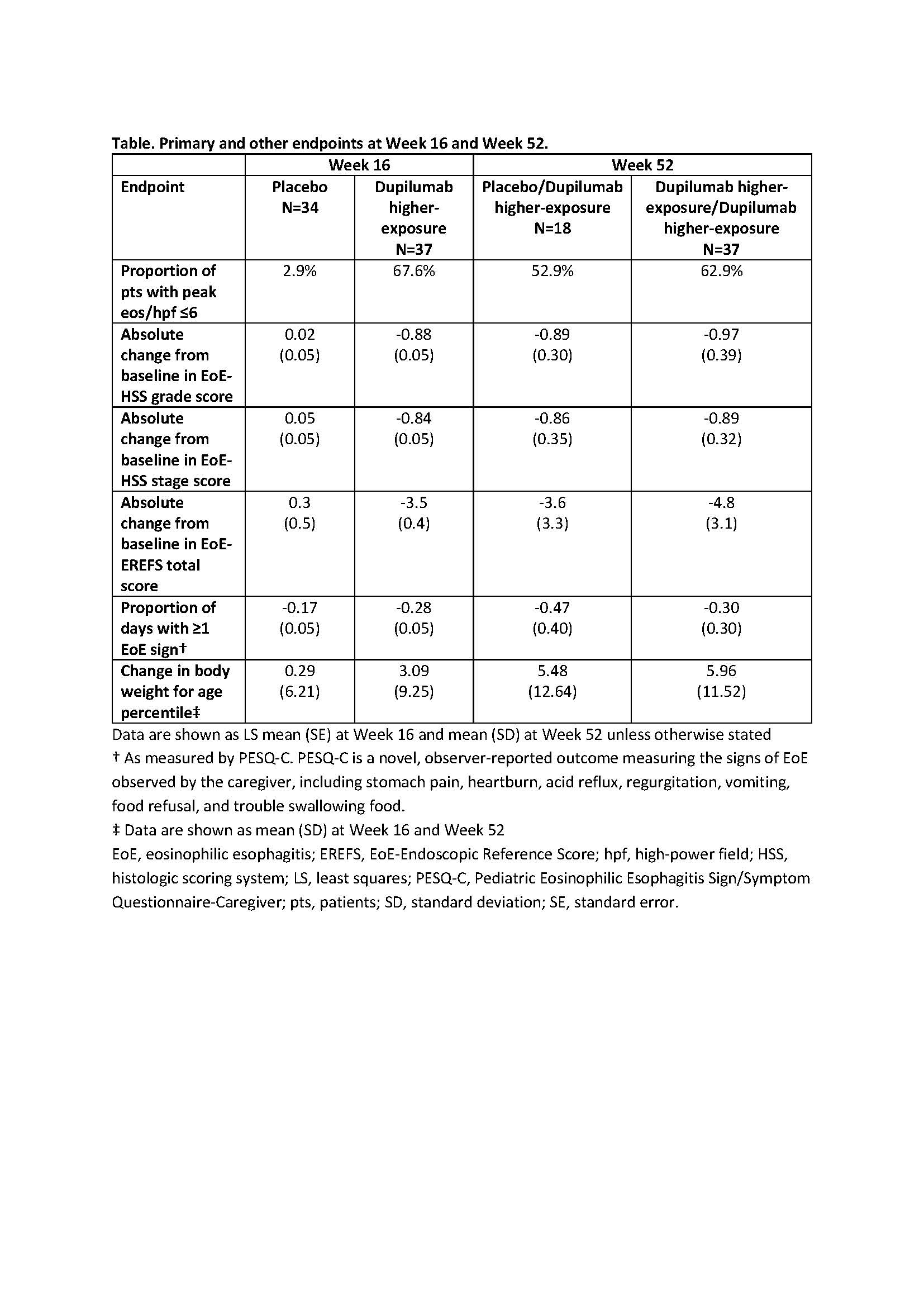
Results: All groups had generally similar baseline demographics, disease characteristics, and a high level of atopic comorbidities. At W16 in Part A, the HE dupilumab group met the primary endpoint of peak esophageal intraepithelial eosinophil (eos) count ≤6 eos/high-power field (hpf) vs placebo (least squares mean difference vs placebo [95% CI], 64.5 [48.19, 80.85], P<0.0001). At W52, 62.9% of pts receiving HE in Parts A and B and 52.9% of pts who switched from placebo in Part A to HE dupilumab in Part B achieved peak eos/hpf ≤6. At W16, the following measures improved from baseline with HE dupilumab vs placebo: EoE-Histologic Scoring System grade and stage scores (–0.88 and –0.84 vs +0.02 and +0.05, both P<0.0001); EoE-Endoscopic Reference Score (–3.5 vs +0.3, P<0.0001); change in body weight for age percentile (+3.09 vs +0.29); and numeric improvement in caregiver-reported proportion of days experiencing ≥1 EoE sign (-0.28 vs -0.17). At W52 in Part B, improvement in these endpoints was maintained or increased with continued HE dupilumab. Improvements were also observed in placebo pts switching to HE dupilumab (Table). At W16, adverse events more frequent with dupilumab vs placebo included COVID-19, rash, headache, and injection site erythema; safety profile was similar through W52.
Discussion: HE dupilumab met the primary endpoint of peak esophageal intraepithelial eos count ≤6 eos/hpf vs placebo and demonstrated significant and clinically meaningful changes in histologic and endoscopic outcomes, and improvements in clinical symptoms and rate of weight gain. Benefits were maintained or increased to W52 with continued treatment.
Acknowledgments: Research sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04394351. We would like to thank Faisal A. Khokhar of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. for their contribution to this analysis. Medical writing/editorial assistance provided by Chris Bulman, PhD, of Adelphi Communications, and funded by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., according to the Good Publication Practice guideline.
Disclosures:
Introduction: There are no approved treatments for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) in children aged <12 years. Dupilumab blocks key type 2 inflammation drivers and is approved for EoE in patients (pts) aged ≥12 years and weighing ≥40kg in the USA. The Phase 3 EoE KIDS trial (NCT04394351) evaluated efficacy and safety of dupilumab in pts aged 1 to <12 years with EoE.
Methods: Part A was a 16 week (W), placebo-controlled study; pts were randomized 2:2:1:1 to weight-tiered, subcutaneous dupilumab on a higher-exposure (HE) or lower-exposure (LE) regimen, or placebo (2 groups). Patients who completed Part A could enter Part B, in which pts continued the same dupilumab regimen and pts on placebo switched to their pre-assigned HE or LE dupilumab dose to W52. This analysis includes pts assigned to HE dupilumab and placebo up to W52.
Results: All groups had generally similar baseline demographics, disease characteristics, and a high level of atopic comorbidities. At W16 in Part A, the HE dupilumab group met the primary endpoint of peak esophageal intraepithelial eosinophil (eos) count ≤6 eos/high-power field (hpf) vs placebo (least squares mean difference vs placebo [95% CI], 64.5 [48.19, 80.85], P<0.0001). At W52, 62.9% of pts receiving HE in Parts A and B and 52.9% of pts who switched from placebo in Part A to HE dupilumab in Part B achieved peak eos/hpf ≤6. At W16, the following measures improved from baseline with HE dupilumab vs placebo: EoE-Histologic Scoring System grade and stage scores (–0.88 and –0.84 vs +0.02 and +0.05, both P<0.0001); EoE-Endoscopic Reference Score (–3.5 vs +0.3, P<0.0001); change in body weight for age percentile (+3.09 vs +0.29); and numeric improvement in caregiver-reported proportion of days experiencing ≥1 EoE sign (-0.28 vs -0.17). At W52 in Part B, improvement in these endpoints was maintained or increased with continued HE dupilumab. Improvements were also observed in placebo pts switching to HE dupilumab (Table). At W16, adverse events more frequent with dupilumab vs placebo included COVID-19, rash, headache, and injection site erythema; safety profile was similar through W52.
Discussion: HE dupilumab met the primary endpoint of peak esophageal intraepithelial eos count ≤6 eos/hpf vs placebo and demonstrated significant and clinically meaningful changes in histologic and endoscopic outcomes, and improvements in clinical symptoms and rate of weight gain. Benefits were maintained or increased to W52 with continued treatment.
Acknowledgments: Research sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04394351. We would like to thank Faisal A. Khokhar of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. for their contribution to this analysis. Medical writing/editorial assistance provided by Chris Bulman, PhD, of Adelphi Communications, and funded by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., according to the Good Publication Practice guideline.

Disclosures:
Mirna Chehade - Consultant, Adare Pharma Solutions/Ellodi, Allakos, AstraZeneca, BMS, Nexstone Immunology, Phathom, Recludix Pharma, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sanofi, Shire/Takeda. Research funding, Adare Pharma Solutions/Ellodi, Allakos, AstraZeneca, Celgene/BMS, Danone, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Shire/Takeda.
Evan Dellon - Research funding, Adare/Ellodi, Allakos, Arena/Pfizer, AstraZeneca, GSK, Meritage, Miraca, Nutricia, Celgene/Receptos/BMS, Regeneron, Revolo, Shire/Takeda. Consultant, Abbott, Abbvie, Adare/Ellodi, Aimmune, Akesobio, Alfasigma, ALK, Allakos, Amgen, Aqilion, Arena/Pfizer, Aslan, AstraZeneca, Avir, Biorasi, Calypso, Celgene/Receptos/BMS, Celldex, Eli Lilly, EsoCap, Eupraxia, Ferring, GSK, Gossamer Bio, Holoclara, Invea, Knightpoint, Landos, LucidDx, Morphic, Nexstone Immunology, Nutricia, Parexel/Calyx, Phathom, Regeneron, Revolo, Robarts/Alimentiv, Salix, Sanofi, Shire/Takeda, Target RWE, Upstream Bio. Educational grant, Allakos, Holoclara, Invea.
Jonathan Spergel - Consultant, Allakos, DBV Technologies, Novartis, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Shire/Takeda. Grant support, DBV Technologies, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Marc Rothenberg - Consultant, Allakos, AstraZeneca, BMS, ClostraBio, PulmOne, Spoon Guru. Equity interest, ClostraBio, PulmOne, Spoon Guru. Royalties, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Mapi Research Trust, PEESSv2, UpToDate. Inventor of patents owned by Cincinnati Children’s Hospital.
Robert Pesek - Consultant, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Margaret Collins - Consultant, Allakos, Arena/Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Calypso Biotech, EsoCap Biotech, GlaxoSmithKline, Receptos/Celgene/BMS, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Robarts Clinical Trials Inc./Alimentiv, Inc. and Shire, a Takeda company.
Ikuo Hirano - Consultant, AbbVie, Adare Pharma Solutions, Allakos, Amgen, Arena Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, BMS, Celgene, Calyx, Celldex Therapeutics, Dermavant, Eli Lilly, Ellodi Pharmaceuticals, EsoCap, Gossamer Bio, Parexel, Receptos/BMS, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sanofi, Shire/Takeda. Research funding, Adare Pharma Solutions, Allakos, AstraZeneca, BMS, Celgene, Ellodi Pharmaceuticals, Meritage, Receptos/BMS, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Shire/Takeda.
Ruiqu Liu - Employee and Shareholder, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Eric Mortensen - Employee and Shareholder, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Jennifer Maloney - Employee and Shareholder, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Eilish McCann - Employee and Shareholder, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Matthew Kosloski - Employee and Shareholder, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Jennifer Hamilton - Employee and Shareholder, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Carin Samuely - Employee and Shareholder, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Arsalan Shabbir - Employee and Shareholder, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Elizabeth Laws - Employee, may hold stock and/or stock options in the company, Sanofi
Renata Martincova - Employee, may hold stock and/or stock options in the company, Sanofi
Lila Glotfelty - Employee, may hold stock and/or stock options in the company, Sanofi.
Mirna Chehade, MD, MPH1, Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH2, Jonathan M. Spergel, MD, PhD3, Marc E. Rothenberg, MD, PhD4, Robert D. Pesek, MD5, Margaret H. Collins, MD4, Ikuo Hirano, MD6, Ruiqi Liu, PhD7, Elizabeth Laws, PhD8, Eric Mortensen, MD7, Renata Martincova, MD9, Jennifer Maloney, MD7, Eilish McCann, PhD7, Matthew P. Kosloski, PharmD, PhD7, Jennifer D. Hamilton, PhD7, Carin Samuely, MD7, Lila Glotfelty, MD, PhD8, Arsalan Shabbir, MD, PhD7. 73 - Dupilumab Improves Histologic and Endoscopic Aspects of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE), as Well as Rate of Weight Gain, in Children Aged 1 to <12 years: 52-week Results From the Phase 3 EoE KIDS Trial (Late-Breaking Abstract), ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Mirna Chehade, MD, MPH1, Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH2, Jonathan M. Spergel, MD, PhD3, Marc E. Rothenberg, MD, PhD4, Robert D. Pesek, MD5, Margaret H. Collins, MD4, Ikuo Hirano, MD6, Ruiqi Liu, PhD7, Elizabeth Laws, PhD8, Eric Mortensen, MD7, Renata Martincova, MD9, Jennifer Maloney, MD7, Eilish McCann, PhD7, Matthew P. Kosloski, PharmD, PhD7, Jennifer D. Hamilton, PhD7, Carin Samuely, MD7, Lila Glotfelty, MD, PhD8, Arsalan Shabbir, MD, PhD7. 73 - Dupilumab Improves Histologic and Endoscopic Aspects of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE), as Well as Rate of Weight Gain, in Children Aged 1 to <12 years: 52-week Results From the Phase 3 EoE KIDS Trial (Late-Breaking Abstract), ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

